Non-equilibrium systems exhibit a wide variety of behaviors, including bifurcations where their properties change dramatically. Despite this variety, a large part of the observed behavior can be understood using methods from dynamical systems and nonlinear physics. A few examples are described below.
Instabilities of ensemble of grains interacting at long distance
Steel grains can be magnetized when plunged in a magnetic field and then interact at large distance. We observed several new instabilities such as a peak forming instability similar
to the Rosensweig instability of ferrofluids or a condensation from a low dense phase to a dense solid like phase.
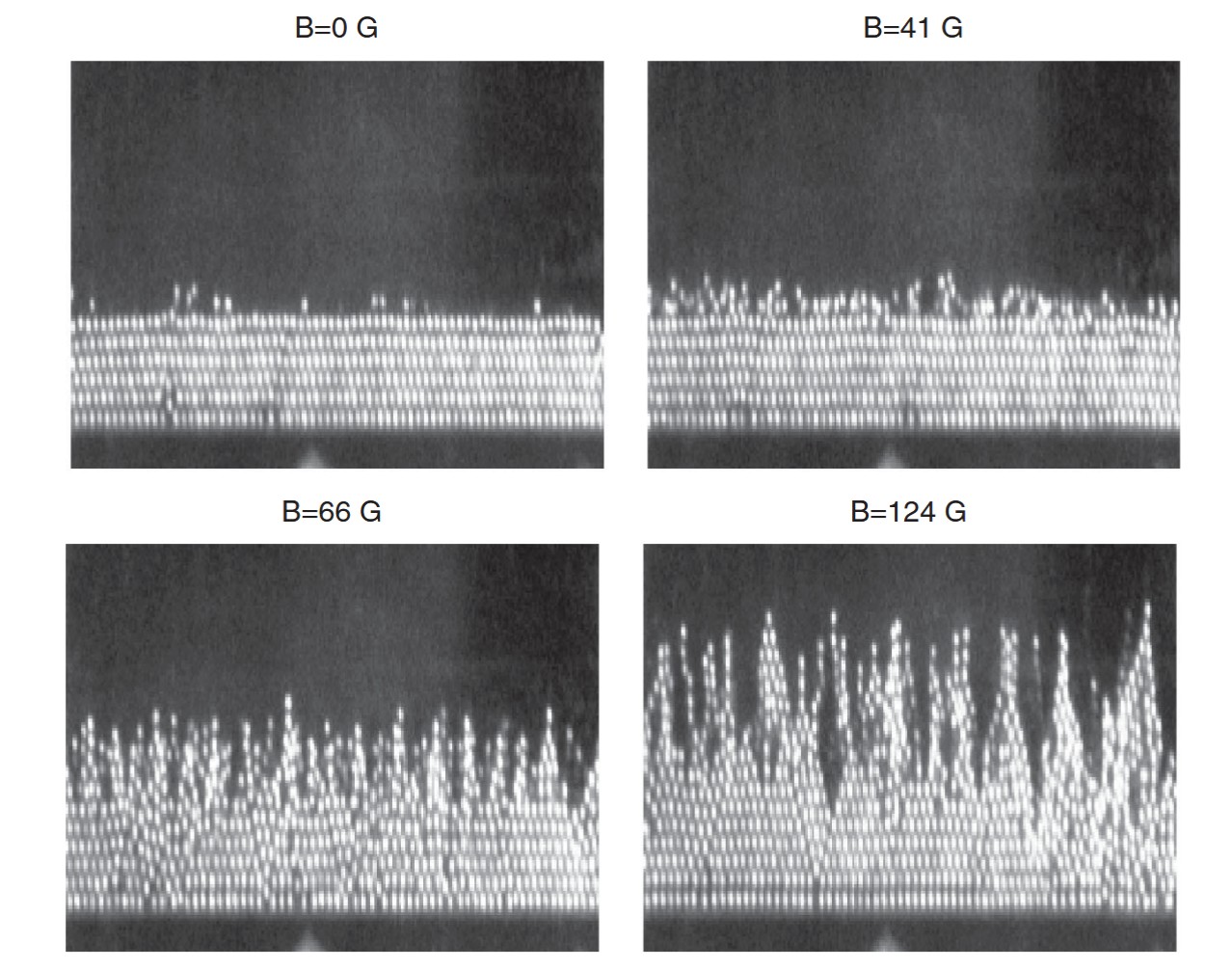
European Physical Journal B (77) 489-492 (2010)
Physical Review Letters, (104) 158001 (2010)
Europhysics Letters (87) 54004 (2009)
Chaotic motors
Universal motors can be used either as a usual motor when current is injected in its coils or as a current generator by dynamo instability
if it is put into rotation.
When a motor is used as a generator and drives a second motor, the system displays several bifurcations such as a standard pitchfork bifurcation
or a Hopf bifurcation.
Above the onsets of these bifuractions, a chaotic dynamic is possible which results from Silnikov’s mechanism of chaos.
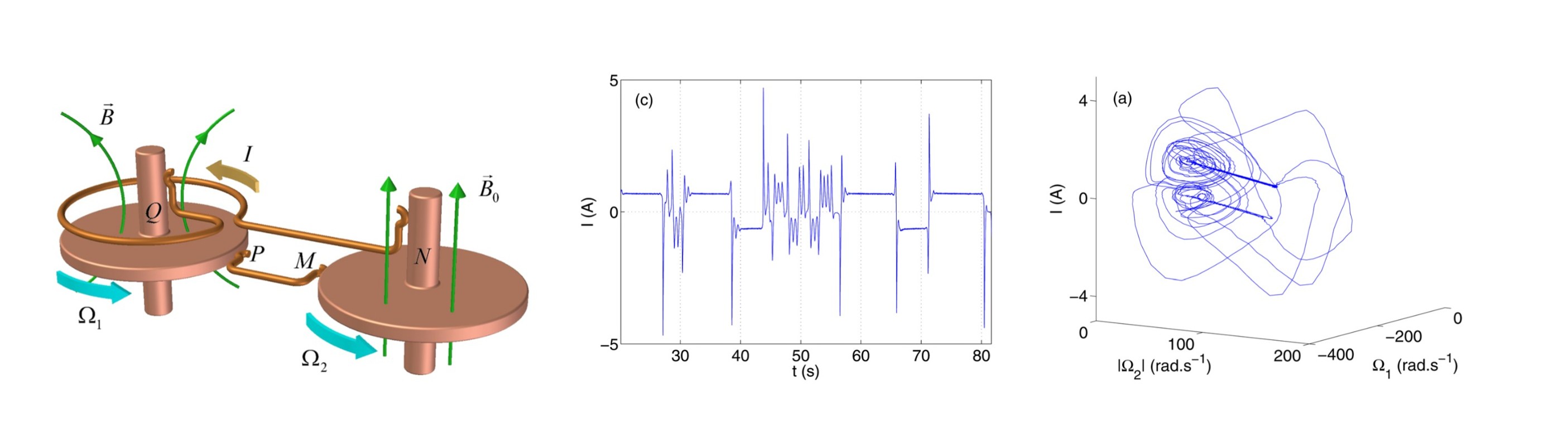
American Journal of Physics (80), 113-121 (2012)
Quasi biennal oscillation
The quasi-biennial oscillation is a periodic change in the direction of winds in the Earth stratosphere.
With a period slightly larger than two years, the wind direction reverses and this occurs all around the Earth.
The mechanism responsible for the formation of the wind relies on internal waves that propagate in density-stratified medium,
such as the stratosphere. Nonlinear effects cause energy transfer from the waves to the large-scale mode
(with zero wave vector and frequency). In some cases, a large-scale flow appears. With B. Semin and S. Fauve,
we conducted an experimental study on the interaction of internal waves with a large-scale flow and observed
the analogous to the QBO: the large scale flow reverses periodically, with a period much larger
than that of the internal waves.
We could understand the nature of the bifurcation and its non linear regimes. In particular bistability can occur.
Observation of the instability and description of its nonlinear regime
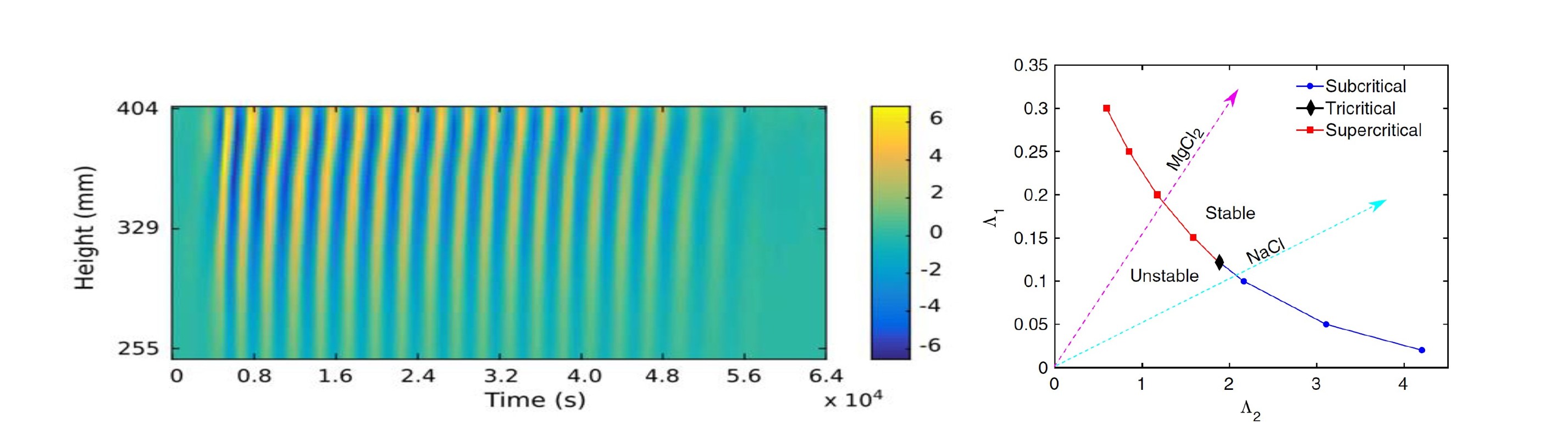
Selected publications
Comptes Rendus. Physique,1-25 (2024)
Physical Review Letters (121), 134502 (2018)
Waves and patterns
European Physical Journal B 35 (3), 291-294 (2003)
Journal of Physical Oceanography 36 (6), 1053-1071 (2006)
Europhysics Letters (112), 54007 (2015)
Physical Review Letters, (116), 174301 (2016)
Physical Review Fluids, (2), 022801 (2017)